 |
 |
POSaM: a fast, flexible, open-source, inkjet oligonucleotide synthesizer and microarrayer.

A DNA array, or gene chip, is an ordered
arrangement of known nucleic acid sequences. Based on the
matching known with unknown sequences, it enables the large-scale
analysis of genes and their products.
There are three varieties of DNA arrays:
macroarrays (nylon filters - plasmid clones - radioactive report
groups), microarrays (glass - PCR or cDNA - fluorescent reporters), and
oligonucleotide arrays (glass - oligonucleotides - fluorescent
reporters). Oligonucleotide array advantages include high
specificity (the ability to distinguish closely-related members of gene
families or alternatively spliced RNAs, gene insertions, gene
deletions, and SNPs) and relatively simple construction (there is no
need for the creation and maintainance of libraries of cDNAs or PCR
products). Inkjet arrays are special oligonucleotide arrays in
which the sequences are synthesized in situ, chemically, on the
surface of the chip.
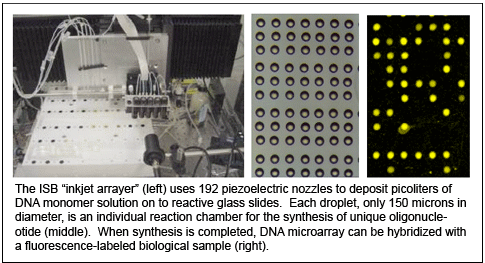
The inkjet array synthesizer produces
custom arrays by combining phosphoramidite DNA synthesis chemistry with
commercial ink-jet technology. The machine uses a six-channel
piezoelectric print head with 32 nozzles per channel to quickly deliver
DNA monomers and activator to thousands of reaction sites on a
silanized glass slide. Each bank of the piezoelectric printer is
attached to a pressurized reservoir containing one phosphoramidite
monomer. The fifth bank delivers activator to the slide, and the sixth
bank can be used for modified phosphoramidite monomers (such as
phosphorylated or fluorescently labeled monomers). The current design
permits the addition of a second 6-channel print head if necessary.
Droplet volume is less than 10 pL and feature size can be less than 40
microns in
diameter with a pitch (center-to-center distance) of less than 150
microns. Typically, features are 150 microns in diameter, have a pitch
of 280 microns, and are printed in numbers of 4900 per chip. The
array substrate is a 25x76mm glass slide. Synthesis occurs inside
a dry, nitrogen-filled chamber.
The Piezoelectric
Oligonucleotide Synthesizer And Microarrayer (POSAM)
was developed in the Hood Laboratory to give researchers access to
customizeable DNA microarrays. The result is an "open source"
platform. The hardware design and protocols are being made
available freely to the public and the control software is released
under the GPL
license. Version 0.6 of Pogo, the control software, is available
below. (Click here
for a screenshot.) The latest version is available through CVS at
Bioinformatics.org.
Requirements:
- Pentium III 500MHz PC
- MS Windows NT 4.0 or later
- Visual Basic Runtime
libraries v.6.0
- National Instruments NIDAQ
v.6.9.1
- Compumotor Com6srvr
v.3.3.1
- POSAM software (one of the following):
Resources for building your own POSAM
- User
manual chapter 1: Assembly
Updated May 2005
New: IEEE-1394 camera for imaging droplets; linear encoders for
precision; fewer parts for droplet detector.
- User manual
chapter 2: Operation
- Slide holder DWG/DXF files
- Acrylic cover DXF files
- Circuit
board design/ordering software
- Circuit board 1503 rev 1.2
Updated
April 2005
Changes: Holes added
for standoffs; traces made thicker.
- Circuit board 1804 rev 1.2
Updated: Aug
2004.
Changes: Missing 30VDC line to pin 15 of DB15 connector added; part
number for 68-pin connector updated; several connector labels added.
- Circuit board 1902 rev 1.2
Updated April
2005
Changes: Photodiode signals at screw terminals; short between
hygrometer and solenoid relay fixed;
7408 chip added to protect LS7183 chip; more labeling on top conductor
layer.
Email us at
|
 |
 |
